- Inicio
- Quem somos
- Produtos
-
Marcas
-
Produtos por Medida
- Analisadores Vibração
- Bombas Peristálticas
- Fluxo de Ar
- CO Monóxido Carbono
- Contadores Geiger
- Destiladores
- Espectrofotometria
- Esterilização
- Fluorescência
- GEOTECNICS
- Umidade do Solo
- Índice de área foliar
- Chuva (pluviométrico)
- Meteorologia
- Nível de Água
- O2 oxigênio
- pH
- Pressão Diferencial
- Radiação
- Salinidade/Condutivid.
- Telemetria
- Velocidade do Ar
- Umidade Relativa
- Veterinary
- PILHAS DE COMBUSTÍVEL
- Analisadores de Redes
- Calibradores
- CAUDAL DE ÁGUA
- Cor / Colorímetro
- Contadores Partículas
- Direçao Vento
- Espectrometria
- Evapotranspiração
- Fotossíntese
- Rachaduras edifícios
- Inspeção de Tubos
- Luz Quântica
- Movimento e GPS
- Nível de diesel
- Oxigênio Dissolvido DO
- Pressão Atmosférica
- Radon
- Savia/Fluxo de Savia
- Temperatura
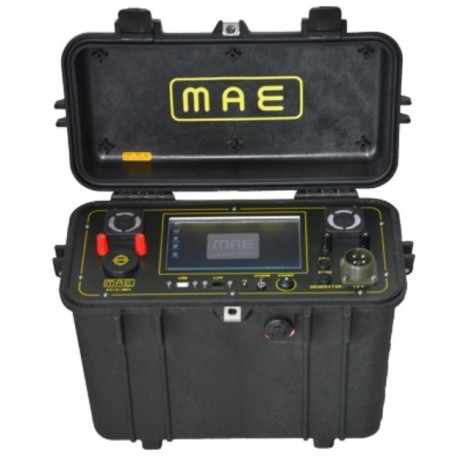
MAE C313SEV Georresistivímetro para medições Quadrupolo
Georresistivímetro para medições quadrupolo
Um georresistivímetro digital é utilizado para levantamentos elétricos V.E.S.Vertical.
Esta unidade caracteriza-se pela sua máxima resolução e precisão em levantamentos geoelétricos e grande rapidez de funcionamento.
Assim que a aquisição de dados estiver concluída, pode ser imediatamente processada com software de processamento de dados relacionado.
A energia de funcionamento é fornecida por uma bateria incorporada e gerida por um microprocessador capaz de proporcionar uma ampla autonomia de aquisição de dados.
A gravação e gravação dos dados ocorre num disco interno ou numa chave USB (fornecida).
A unidade é totalmente informatizada e todas as suas funções de funcionamento são selecionadas simplesmente através de um menu tátil no monitor LCD a cores de 7" com ecrã tátil integrado.
■ Número de elétrodos: 4
■ Fonte de alimentação: Bateria interna de 12 V, bateria externa
■ Consumo médio de energia: 2,5A, pico de 50A
■ Autonomia média: 9 horas
■ Condições ambientais de funcionamento: -20/80 °C
■ Resolução: 24 bits
■ Caixa: Polipropileno, válvula de pressão automática, IP67
■ Visor: LCD de 7" touchscreen integrado
■ Sistema operativo: Windows 10
■ Portas: LAN, USB
■ Gravação de dados: SSD interno, pen USB externa
■ Formato de dados: TSV, CSV, DAT
■ Dimensões: 49 x 19 x 26,4 cm
■ Peso: 9,6 Kg
Corrente de saída:
■ Regulamento: Automático 5 passos
■ Intensidade máxima: 5A a 50V
■ Tensão de saída: ±50V, ±100V, ±250V, ±500V, ±800V
■ Potência máxima: 250W
■ Tempo de injeção: configurável a partir de 0,25 seg. (visualização gráfica da onda)
■ Medir com precisão: ±0,2μA
Medição potencial:
■ Alcance: Alcance automático
■ Medida: medição simultânea em todos os canais
■ Escala completa máxima: ±25V
■ Impedância de entrada: 2,5 MOHM
■ Filtro de frequência de rede: 50 Hz
■ Proteção: superior
■ Precisão da medição: ±1,5μV dentro do intervalo de ±25V
■ Redução de ruído: média de 2 a 10 medições
■ Reinicialização automática do potencial espontâneo: Automático
■ Precisão da resistividade medida: ±0,5%
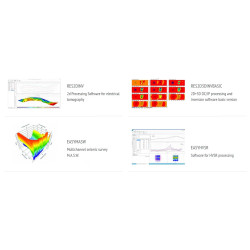
V.E.S. Vertical Electrical Survey+
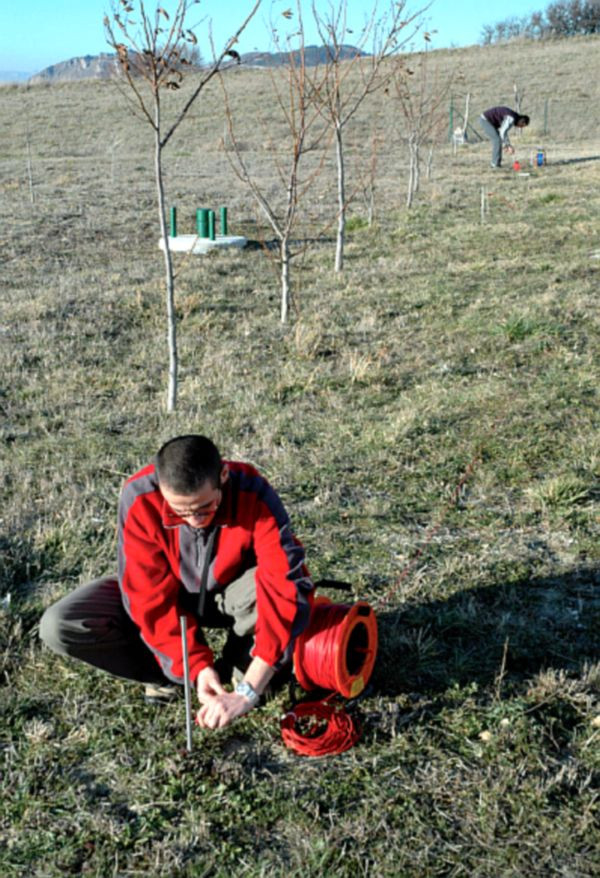

Induced Polarization (IP) is an electrical phenomenon that occurs within material media. In the time domain, it is observed as chargeability, which happens when stress is released after the interruption of a step-type electric current. In the frequency domain, it involves the dispersion of electrical resistivity as the frequency of an alternating current changes. IP sources are primarily linked to redox processes at the interfaces between metal grains and interstitial fluids (electrode polarization). Another significant IP source is the accumulation of ions in moving electrolytes due to variations in mobility along the path (electro-kinetic polarization). Through tomographic inversion of surface data, the resulting images reflect chargeability, enabling the identification of areas with potential hydrocarbon accumulations or other significant concentrations. Chargeability is directly proportional to the amount of charge stored by the lithotype, indicating the concentration of conductive materials in the multi-electrode area. Induced Polarization Measurement+
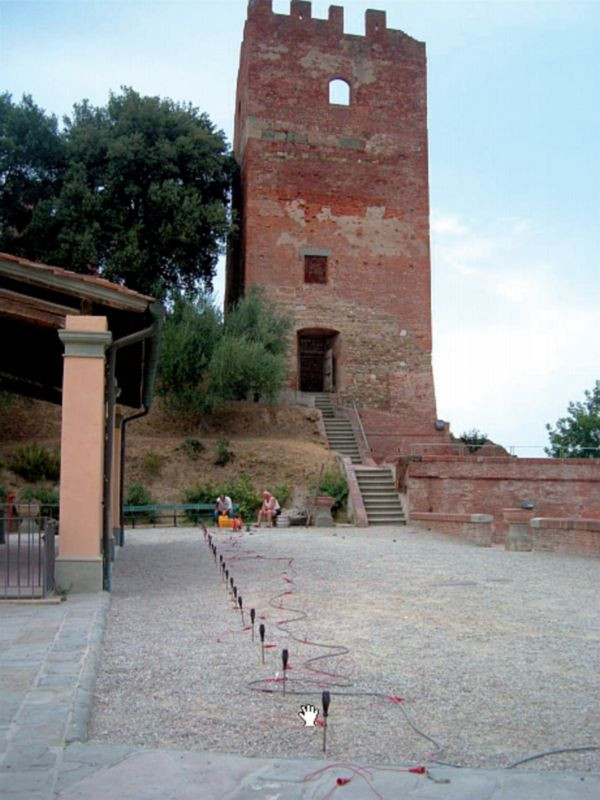

The Spontaneous Potential (SP) method involves measuring potential differences on the surface that are associated with natural electric fields, which are linked to the underground flow of aqueous electrolytic solutions in porous media. By analyzing SP anomalies on the surface, the intensity and position of ionic charge concentrations of both polarities can be determined. The test involves placing two electrodes: one near the measurement station and the other moved along subsequent stations on the line. Alternatively, both electrodes can be moved while maintaining a consistent interval between them, mapping the ground based on spontaneous potential variations. This method is particularly useful in mining for locating sulfides and graphite, as well as in archaeology. Underground water flows can be influenced by archaeological structures, which may act as drains or obstacles. By identifying SP anomalies, it is possible to indirectly detect these underground structures. Spontaneous Potential Measurement+

- Tipo de Instrumento
- Georresistivímetro